When it comes to keeping your vehicle running smoothly, understanding the components under the hood is crucial. Two essential belts play pivotal roles in your car’s performance: the serpentine belt and the timing belt. But what’s the difference between them? Knowing this can save you time and money on repairs and maintenance.
The serpentine belt powers multiple accessories like the alternator and air conditioning compressor, while the timing belt ensures your engine’s valves open and close at the right time. Confusing these two can lead to costly mistakes. Jump into the details and empower yourself with knowledge that keeps your engine humming and your wallet happy.
Understanding Serpentine Belts
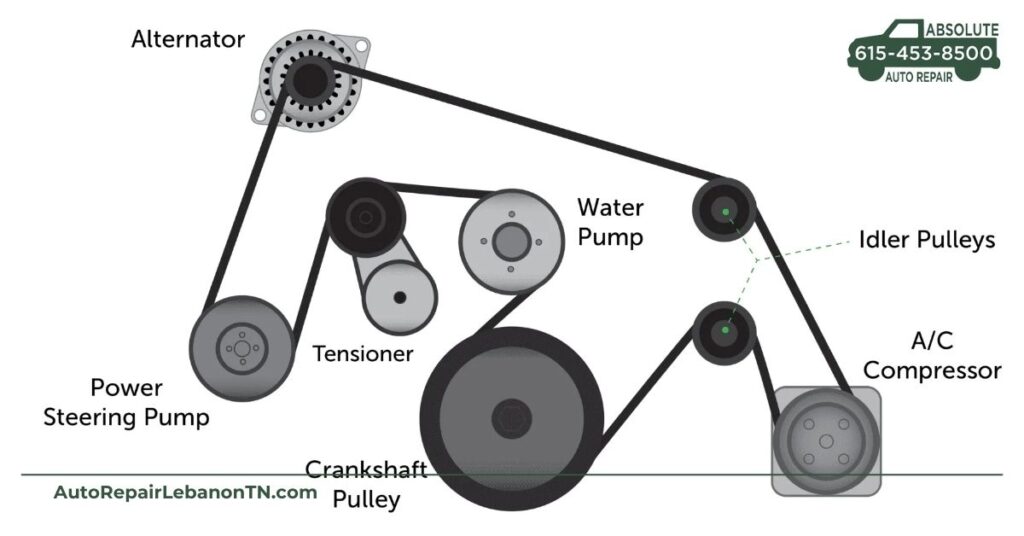
Serpentine belts play a crucial role in your vehicle’s performance. These belts connect various engine accessories and ensure they operate smoothly.
Definition and Function
A serpentine belt is a single, continuous belt that powers multiple accessories within the engine. This includes the alternator, power steering pump, water pump, and air conditioning compressor. By transferring power from the engine’s crankshaft to these components, it helps in maintaining proper vehicle function. If the serpentine belt fails, you may encounter issues like a dead battery, loss of steering control, and overheating.
Components of Serpentine Belts
Several key components make up serpentine belts. Primary materials include rubber and reinforced fibers, both providing flexibility and strength. When you observe the belt, you’ll notice it has grooves or ridges along its length. These features enhance grip on the pulleys, minimizing slippage during operation. Also, tensioners and idler pulleys are part of the system, ensuring the belt maintains appropriate tension for optimal performance. Regular inspection of these components helps prevent unexpected failures.
Understanding Timing Belts
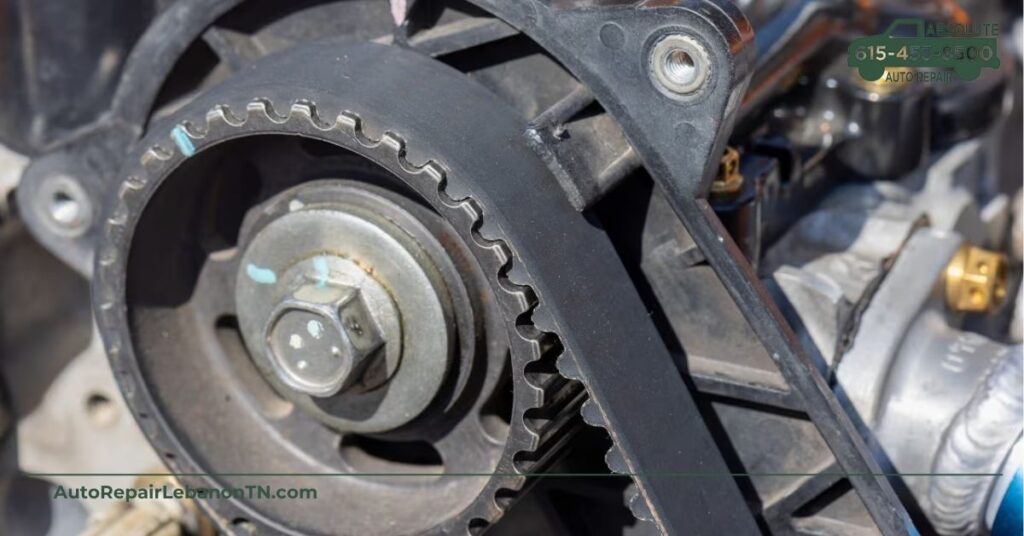

Gaining knowledge about timing belts helps you understand their critical role in vehicle mechanics. These belts regulate the engine’s valve timing, ensuring smooth engine performance.
Definition and Function
A timing belt connects the crankshaft to the camshaft. This relationship allows for the synchronized movement of engine valves. When properly functioning, the timing belt contributes to optimal engine performance. Failure to maintain the timing belt can lead to severe engine damage, such as bent valves or piston damage.
Components of Timing Belts
Several components contribute to the effectiveness of timing belts. Durable materials like neoprene or polyurethane enhance their longevity. Horizontal teeth on the belt fit precisely on the crankshaft and camshaft to maintain timing accuracy. Tensioners and idler pulleys help maintain the correct tension, preventing slippage or misalignment. Regular inspection of these components ensures your engine runs smoothly without costly issues arising.
Key Differences Between Serpentine Belt and Timing Belt
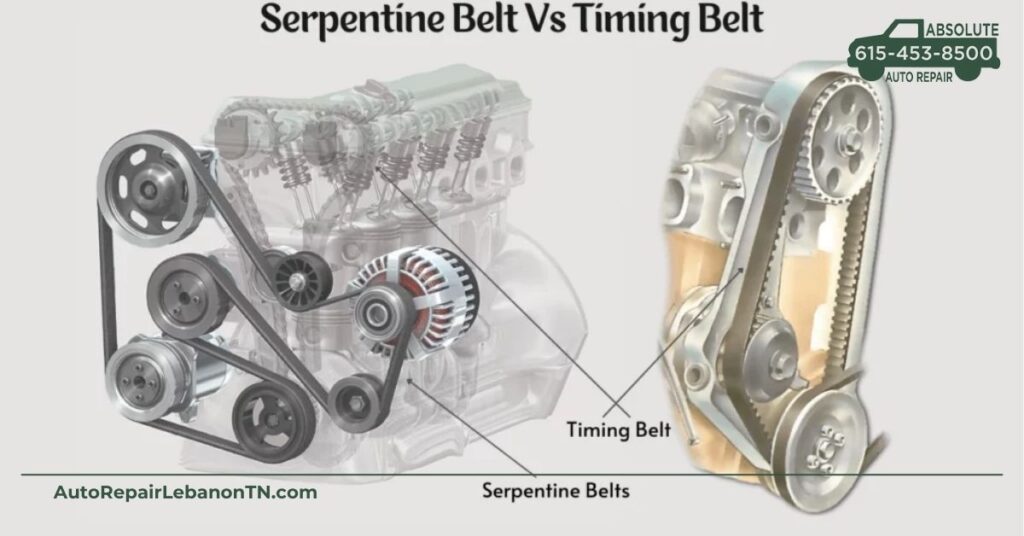
Understanding the key differences between the serpentine belt and timing belt helps in vehicle maintenance. Each belt serves distinct functions, installation processes, and replacement timelines.
Functionality
Serpentine belts power essential engine accessories. These accessories include the alternator, power steering pump, coolant pump, and air conditioning compressor. Timing belts, in contrast, regulate the timing of engine valves. This synchronization is crucial for preventing engine damage during the combustion cycle.
Installation and Maintenance
Installing a serpentine belt is straightforward. Its location on the exterior of the engine makes it visible, allowing for easy access. Maintenance involves regular inspections to identify wear or tension issues. Timing belts require more involved installation. Positioned inside the engine, their maintenance focuses on precise timing and alignment. Regular checks help avert severe engine damage caused by timing issues.
Lifespan and Replacement
Typically, a serpentine belt lasts between 50,000 to 100,000 miles. Scheduling replacements according to your vehicle’s specifications prevents unexpected failures. In contrast, timing belts often need replacement every 60,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on the manufacturer’s guidelines. Neglecting to replace a worn timing belt can lead to extensive engine repairs. Regular replacement of both belts ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of serpentine belts and timing belts helps you make informed maintenance decisions. Below are key benefits for each type of belt.
Benefits of Serpentine Belts
- Efficiency emerges as a primary advantage, as serpentine belts operate more effectively than older multiple belt systems. This design results in a smaller footprint within the engine compartment, allowing for better space utilization.
- Reduced slip is important, improving both belt life and mechanical efficiency. When belts maintain proper tension, they deliver consistent power to all connected accessories.
- Installation and replacement processes are generally simpler, which can lead to lower labor costs. You can often access the serpentine belt without removing other engine components.
Benefits of Timing Belts
- Precision timing is essential for effective engine performance. Timing belts ensure the synchronized rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft, crucial for proper valve function.
- Durability in materials plays a vital role, as timing belts are typically made from heavy-duty synthetic materials. Such construction allows them to withstand high temperatures and stress during engine operation.
- Maintenance intervals provide an advantage, with recommended replacement timelines ranging from 60,000 to 100,000 miles. Keeping track of these intervals can prevent serious engine damage caused by belt failure.
Understanding these benefits empowers you to maintain your vehicle effectively. Taking proper care of both serpentine and timing belts promotes optimal vehicle performance and longevity.
Conclusion
Being aware of the differences between the serpentine belt and timing belt can save you from costly repairs and ensure your vehicle runs smoothly. Each belt plays a vital role in your car’s performance. Regular inspections and timely replacements are crucial for maintaining these components.
By understanding their functions and maintenance needs, you’re better equipped to keep your vehicle in top shape. Don’t overlook these essential parts; staying informed can lead to a longer-lasting and more reliable vehicle. Make vehicle care a priority and enjoy the benefits of smooth driving.
Frequently Asked Questions
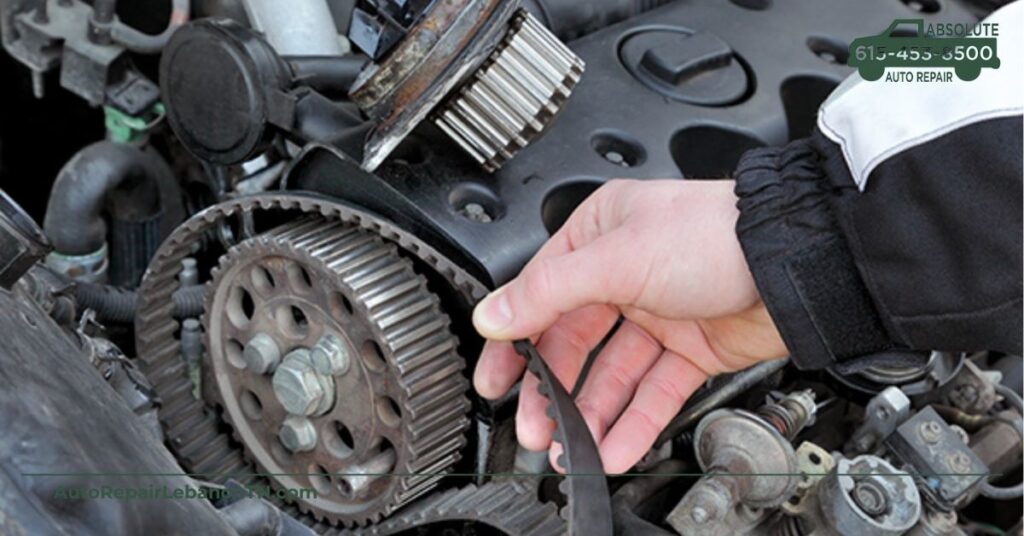

What is the purpose of the serpentine belt in a vehicle?
The serpentine belt powers multiple accessories in a vehicle, such as the alternator, power steering pump, water pump, and air conditioning compressor. It connects to the engine’s crankshaft and is crucial for efficient vehicle performance.
How does a timing belt function?
A timing belt regulates the engine’s valve timing by connecting the crankshaft and camshaft. This synchronization ensures that engine valves open and close at the correct intervals, which is vital for smooth engine performance.
What are the main differences between a serpentine belt and a timing belt?
The main differences lie in their functions and installation. The serpentine belt powers accessories, while the timing belt regulates valve timing. Installation of a serpentine belt is simpler, as it’s located externally, whereas a timing belt requires disassembly of engine components.
How often should a serpentine belt be replaced?
Typically, a serpentine belt should be replaced every 50,000 to 100,000 miles. Regular inspection is advised to catch signs of wear, as a failure can lead to significant vehicle issues.
When should a timing belt be replaced?
Timing belts usually require replacement every 60,000 to 100,000 miles. Regular maintenance is essential, as neglecting it can lead to severe engine damage, including bent valves or piston issues.
What materials are serpentine and timing belts made from?
Serpentine belts are typically made from rubber reinforced with fiber, while timing belts are often made from neoprene or polyurethane, featuring horizontal teeth for precise fitting.
What happens if a serpentine or timing belt fails?
A serpentine belt failure can lead to loss of power steering, overheating, or a dead battery. A timing belt failure can cause severe engine damage, leading to costly repairs, such as bent valves or damaged pistons.
How can I maintain my vehicle’s belts?
Regular inspection and timely replacements are crucial for maintaining both serpentine and timing belts. Check for signs of wear, such as cracking or fraying, and consult a mechanic for specific maintenance recommendations.

