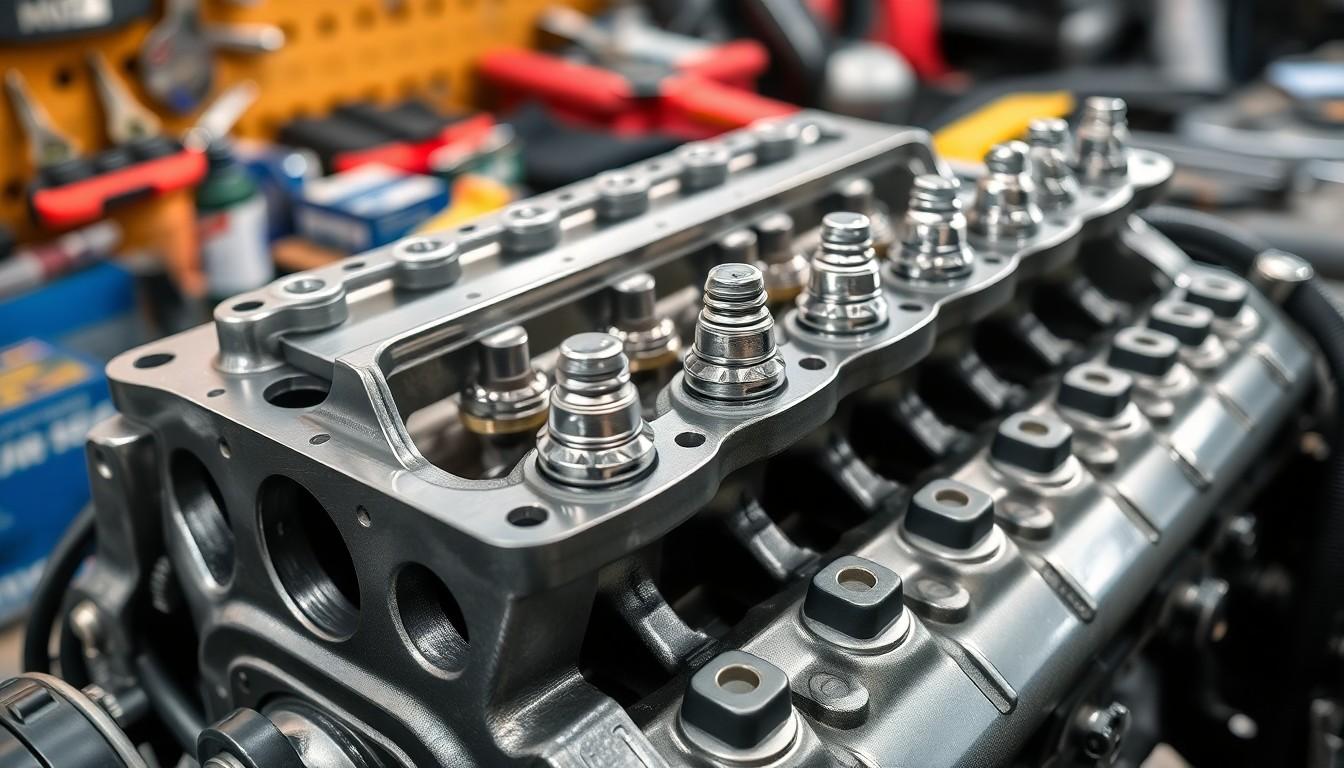
Ever wondered what makes your car engine run smoothly? The cylinder head is one of those critical components that many drivers overlook until something goes wrong. It’s the metal component that sits atop your engine block, sealing the combustion chambers and playing a crucial role in your vehicle’s performance.
We’ve found that understanding your cylinder head’s function can save you thousands in unnecessary repairs. This vital engine part houses the valves, spark plugs, and fuel injectors while managing airflow and maintaining proper compression. Without a properly functioning cylinder head, your engine simply wouldn’t operate efficiently—or at all.
The Core Function of a Cylinder Head in an Engine
The cylinder head forms the upper section of the engine block and serves as a critical sealing component for the combustion chamber. Located atop the engine block, it creates an airtight seal that contains the immense pressure generated during combustion. This containment is essential for converting fuel energy into mechanical power effectively.
Cylinder heads manage the flow of gases in and out of the combustion chamber through precisely engineered passages. Air and fuel mixtures enter through intake ports, while exhaust gases exit through exhaust ports, creating a continuous cycle that powers the engine. These flow paths are carefully designed to optimize engine performance based on exact vehicle requirements.
Beyond sealing and directing gas flow, cylinder heads house several crucial engine components. Valves, valve springs, spark plugs, and fuel injectors all reside within the cylinder head assembly. The integration of these components in a single unit allows for efficient operation and simplified engine design.
Temperature regulation represents another vital function of cylinder heads. Most modern cylinder heads incorporate water jackets—channels that allow coolant to circulate around the combustion chamber. This cooling system prevents overheating by transferring heat away from the combustion chambers, maintaining optimal operating temperatures even under demanding conditions.
Cylinder heads contribute significantly to an engine’s compression ratio by defining the volume of the combustion chamber. The exact design and shape of the combustion chamber in the cylinder head affect how efficiently the air-fuel mixture burns, directly impacting engine power, fuel economy, and emissions performance.
Anatomy of a Cylinder Head: Key Components
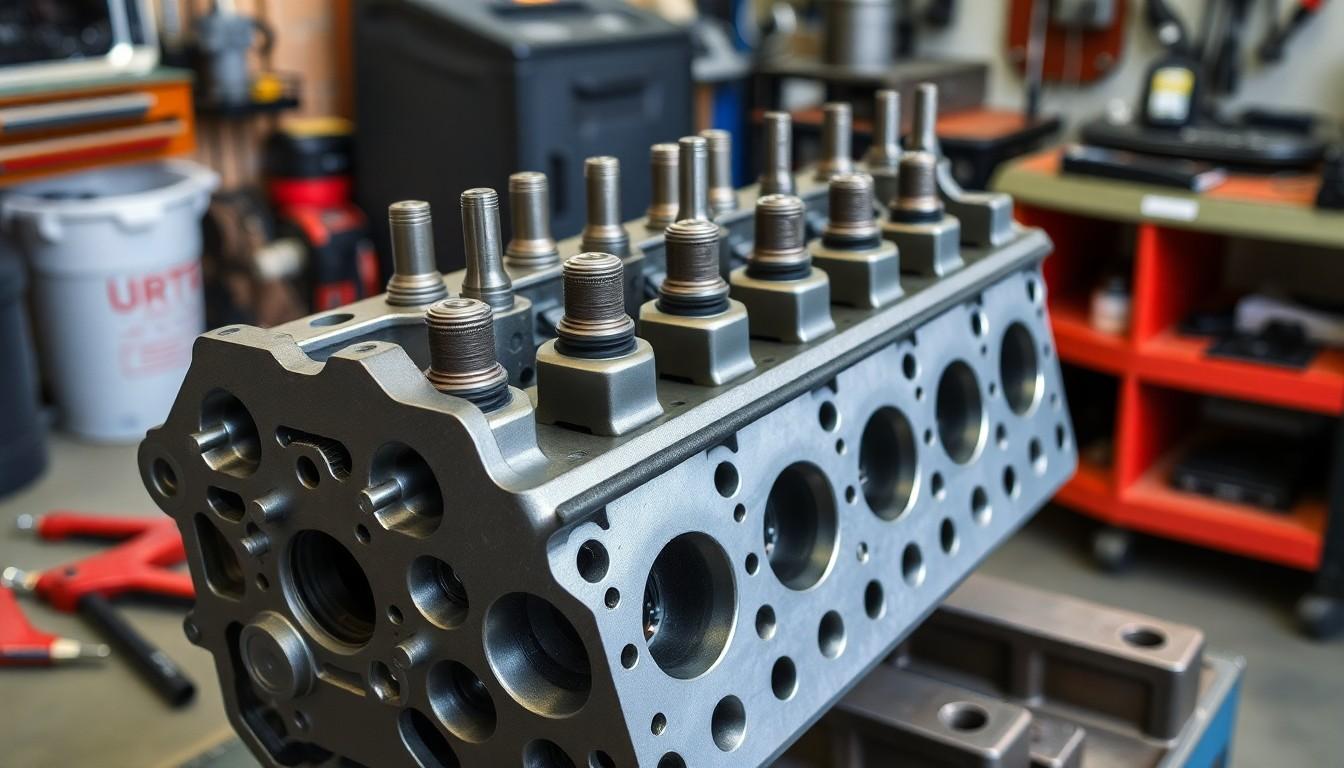

The cylinder head’s complex structure contains several critical components that work together to enable proper engine function. Understanding these elements helps explain how this crucial part facilitates the engine’s operation and performance.
Valves and Valve Seats
Valves control the flow of gases into and out of the combustion chamber, serving as gatekeepers for the engine’s breathing process. Intake valves open to allow the air-fuel mixture to enter the cylinder, while exhaust valves release spent gases after combustion occurs. These valves rest on precisely machined surfaces called valve seats when closed, creating an airtight seal that prevents pressure loss during compression and combustion cycles. The valve assembly includes springs and lifters that ensure proper valve timing and operation throughout various engine speeds.
Intake and Exhaust Ports
Intake ports channel the air-fuel mixture from the intake manifold directly to the combustion chamber through carefully designed passages in the cylinder head. These pathways are engineered with exact shapes and dimensions to optimize airflow velocity and volume, improving the engine’s breathing capability. Exhaust ports, located on the opposite side, form passages that direct combustion byproducts away from the cylinder and into the exhaust system. The design of these ports significantly impacts engine performance, with larger or more efficiently shaped ports typically allowing better gas flow for increased power output.
Combustion Chambers
Combustion chambers form the space where the controlled explosion of fuel and air generates power to drive the vehicle. The chamber’s shape, size, and design directly influence how efficiently fuel burns and how effectively the energy transfers to the pistons. Modern combustion chamber designs focus on promoting complete fuel burning while minimizing knocking and pre-ignition issues. The chamber walls must withstand extreme heat and pressure variations that occur with each combustion cycle. Engine manufacturers create various combustion chamber configurations—such as hemispherical, pentroof, or wedge designs—each offering different performance characteristics for exact applications.
How a Cylinder Head Works in the Combustion Process
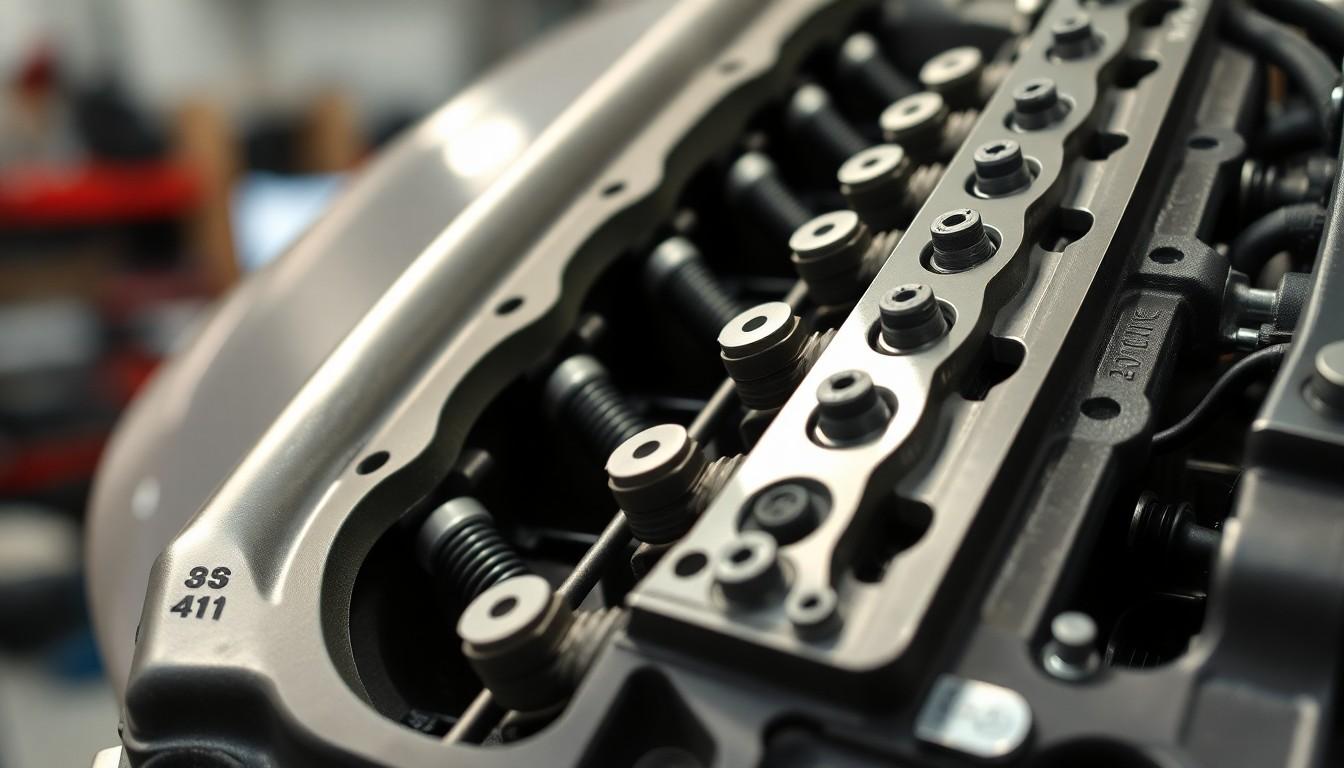

The cylinder head serves as the mechanical control center of an internal combustion engine. It sits atop the engine block, forming the roof of the combustion chamber and integrating multiple critical systems necessary for the engine’s operation.
Controlling Air-Fuel Mixture Flow
Cylinder heads contain strategically designed passages and ports that optimize the air-fuel mixture’s journey into the combustion chamber. These pathways aren’t merely hollow tunnels but precisely engineered channels that enhance flow dynamics, ensuring the proper mixture reaches each cylinder at the ideal moment. Intake valves housed within the cylinder head regulate the entry timing of this mixture, opening and closing at exact intervals determined by the camshaft rotation. The mechanical components in the cylinder head, including valve springs and lifters, work in concert to maintain this precise timing sequence across all engine speeds and loads. Performance engines often feature cylinder heads with larger or redesigned intake ports to maximize airflow capacity, directly impacting the engine’s power output and efficiency.
Managing Exhaust Gas Release
Cylinder heads control the evacuation of exhaust gases through dedicated valves and ports that activate after the combustion process completes. The exhaust valves open at predetermined timing intervals, allowing spent gases to exit the combustion chamber and flow through exhaust ports toward the exhaust manifold. Efficient exhaust gas flow represents a critical function of well-designed cylinder heads, as any restriction in this system can reduce engine performance and increase harmful emissions. The size, shape, and surface finish of exhaust ports significantly influence the engine’s breathing capability, with smoother, more direct pathways promoting better scavenging of exhaust gases. Modern cylinder heads incorporate advanced port designs that balance flow velocity with volume capacity to optimize exhaust gas release across the engine’s operating range.
Different Types of Cylinder Heads
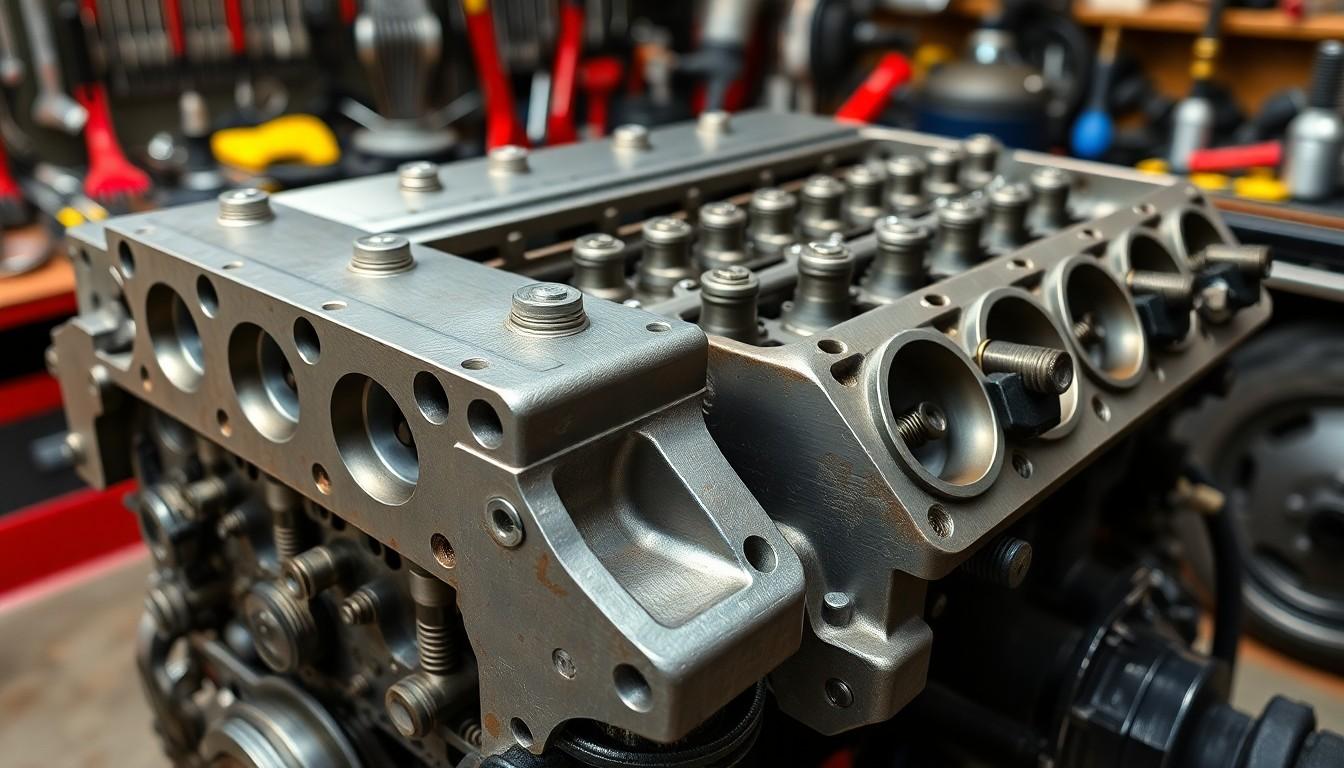
Cylinder heads come in various designs to accommodate different engine configurations and performance requirements. Each type offers exact advantages in terms of efficiency, power output, and manufacturing complexity.
Overhead Valve Designs
Overhead valve (OHV) designs represent a traditional cylinder head configuration where the valves are positioned above the combustion chamber. In these systems, the camshaft remains in the engine block rather than in the cylinder head itself. Operation occurs through a series of mechanical components including lifters, pushrods, and rocker arms that transfer motion from the camshaft to the valves. OHV designs offer several practical advantages, including reduced manufacturing costs and a more compact overall engine height. This configuration creates an engine that’s less expensive to produce while maintaining decent reliability for everyday driving applications. Though simpler than other designs, OHV setups typically can’t match the efficiency and high-RPM performance of overhead camshaft configurations due to the increased reciprocating mass and indirect valve actuation.
Overhead Camshaft Configurations
Overhead camshaft (OHC) configurations position the camshaft directly within the cylinder head, providing more direct control over valve operation. This arrangement reduces the number of moving parts in the valvetrain and allows for more precise valve timing and lift. OHC designs fall into two primary categories: Single Overhead Camshaft (SOHC) and Dual Overhead Camshaft (DOHC). SOHC engines use one camshaft to operate both intake and exhaust valves, striking a balance between performance and complexity. DOHC systems employ separate camshafts for intake and exhaust valves, enabling even greater precision in valve control and timing. The direct actuation of valves in OHC designs permits higher engine speeds and improved volumetric efficiency compared to OHV configurations. Modern performance engines predominantly use DOHC arrangements to maximize power output and efficiency, especially in applications where high-RPM operation is desirable.
Common Cylinder Head Problems and Symptoms
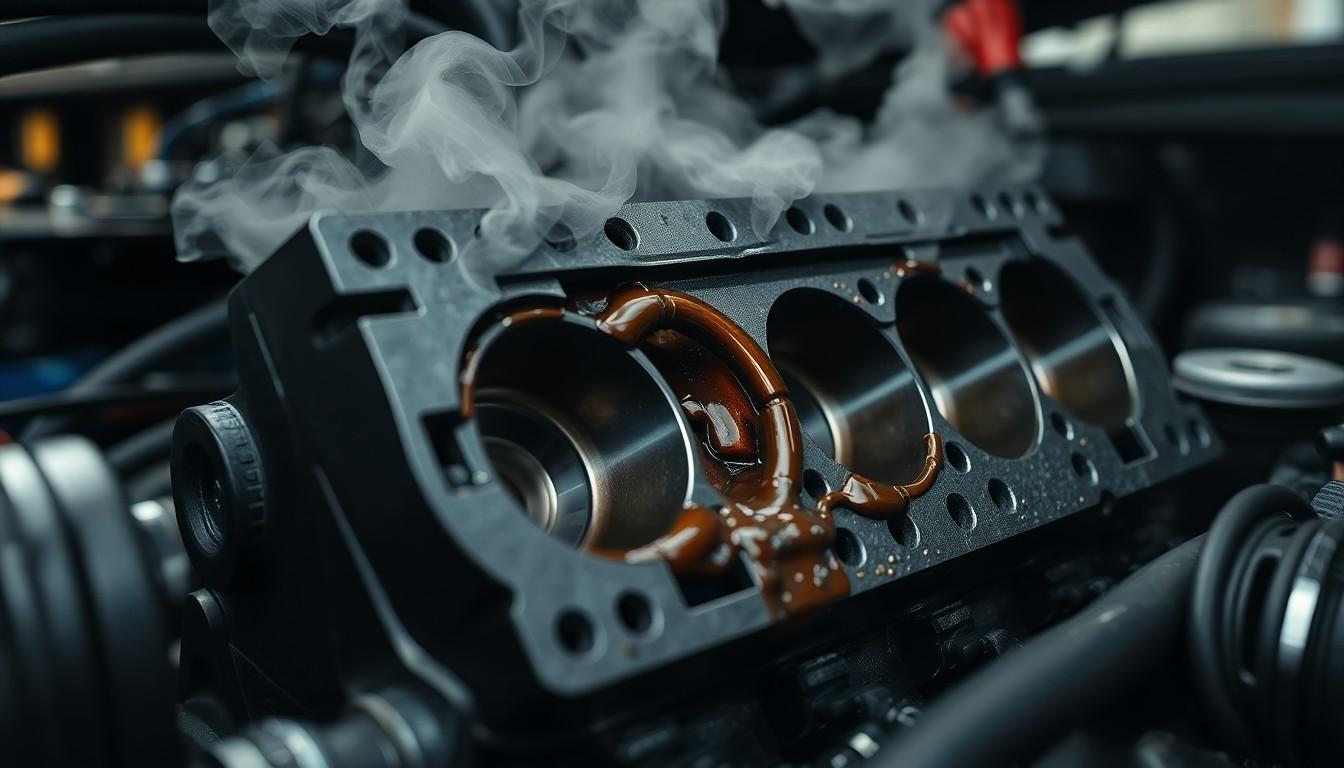
Cylinder head failures represent some of the most serious engine issues vehicle owners encounter. These problems often manifest through exact symptoms that signal potential damage requiring immediate attention.
Cracked Cylinder Head Warning Signs
Cracked cylinder heads typically result from engine overheating, warping, or physical damage to the component. When a crack develops, several telltale symptoms appear: coolant leaking into the combustion chamber or oil system, white smoke billowing from the exhaust pipe, and persistent engine overheating even though proper coolant levels. Performance issues become noticeable through power loss during acceleration or rough idling. The most definitive evidence often appears as contamination—oil and coolant mixing together, visible as a milky substance in either the oil or coolant reservoirs.
Gasket Failure Issues
Head gasket failures stem from worn-out materials, improper installation during previous repairs, or repeated engine overheating cycles. Identifying gasket problems involves looking for visible coolant or oil leaks around the cylinder head sealing surfaces. Bubbles appearing in the coolant reservoir while the engine runs indicate air entering the cooling system through gasket breaches. White smoke emissions from the exhaust pipe signal coolant burning in the combustion chamber due to gasket failure. Engine performance suffers significantly as compression loss occurs between cylinders, resulting in rough running, misfires, and decreased power output.
Other common cylinder head issues include warping from excessive heat exposure, which prevents proper sealing against the engine block. Corrosion can develop on cylinder head surfaces over time, particularly in cooling system passages, leading to restricted coolant flow and subsequent overheating. Valve-related problems within the cylinder head assembly—such as burned valves, worn valve guides, or broken valve springs—create additional performance issues that compromise engine efficiency and reliability.
Maintaining Your Cylinder Head for Engine Longevity
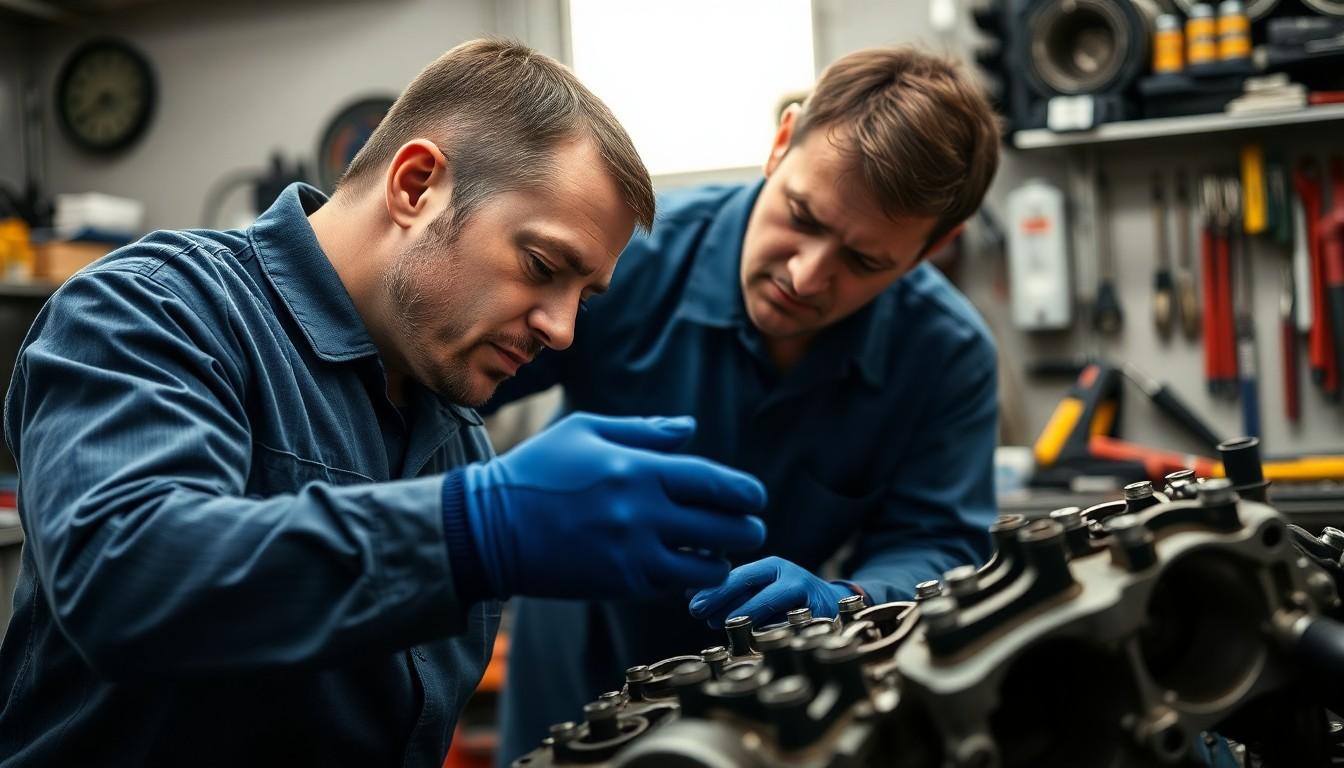

Regular inspection forms the foundation of proper cylinder head maintenance. Checking for signs of wear including cracks, warping, and head gasket leaks prevents minor issues from becoming major repairs. Physical damage often appears as hairline fractures or visible deformation that compromises the seal between the cylinder head and engine block.
Coolant system maintenance ensures your engine operates at optimal temperatures. Flush and replace coolant according to manufacturer recommendations to prevent buildup of sediment and corrosion that can damage water jackets within the cylinder head. Proper coolant levels and quality directly protect against overheating, which is the leading cause of cylinder head failure.
Lubrication plays a critical role in cylinder head longevity. Consistent oil changes using the correct grade and type of oil keep moving components functioning smoothly. Engine oil not only lubricates valves and other cylinder head components but also helps transfer heat away from critical areas, reducing thermal stress.
Valve maintenance requires periodic inspection and adjustment. Intake and exhaust valves undergo tremendous stress during normal operation, making regular maintenance essential for proper sealing and optimal engine performance. Carbon buildup on valves restricts airflow and reduces efficiency, particularly in direct injection engines.
Temperature management through proper driving habits extends cylinder head life. Allowing your engine to reach operating temperature before demanding high performance prevents thermal shock to cylinder head components. Similarly, cool-down periods after high-load driving give the cylinder head time to dissipate heat evenly.
Conclusion
The cylinder head truly stands as the unsung hero of your engine’s performance and longevity. Acting as both gatekeeper and command center it orchestrates the complex dance of air fuel and exhaust while housing critical components that keep your vehicle running smoothly.
Regular maintenance of your cylinder head isn’t just recommended—it’s essential for preventing costly repairs and ensuring optimal engine efficiency. By understanding its functions and recognizing warning signs of potential issues you’ll be better equipped to protect this vital component.
Remember that proper driving habits along with routine inspections can significantly extend your engine’s life. Your cylinder head may be just one part of a complex system but it’s undeniably at the heart of your vehicle’s performance and reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a cylinder head and why is it important?
A cylinder head is the upper section of an engine block that seals the combustion chambers and houses vital components like valves, spark plugs, and fuel injectors. It’s crucial because it manages airflow and compression, directly affecting engine performance and efficiency. A properly functioning cylinder head ensures optimal power output and fuel economy, while a damaged one can lead to severe engine problems and costly repairs.
How does a cylinder head affect engine performance?
The cylinder head directly impacts engine performance by controlling airflow into and out of combustion chambers through precisely engineered passages. It affects the engine’s compression ratio, which determines power output and fuel efficiency. The design of intake and exhaust ports influences how effectively air enters and exits the engine. Additionally, well-designed combustion chambers optimize the fuel-air mixture for better combustion and energy transfer.
What are the main components of a cylinder head?
The main components include valves (intake and exhaust) that control gas flow, valve seats that provide sealing surfaces, valve springs that return valves to closed positions, intake and exhaust ports that channel gases, combustion chambers where fuel-air mixture ignites, spark plug holes, and water jackets for cooling. Some cylinder heads also contain camshafts, rocker arms, and fuel injectors depending on the engine design.
What’s the difference between OHV and OHC cylinder heads?
Overhead Valve (OHV) designs position valves above the combustion chamber but place the camshaft in the engine block, offering lower manufacturing costs and compact engine height. Overhead Camshaft (OHC) designs locate the camshaft directly in the cylinder head for more precise valve control and higher engine speeds. OHC comes in two variations: Single (SOHC) with one camshaft and Dual (DOHC) with separate camshafts for intake and exhaust valves.
How can I tell if my cylinder head is failing?
Signs of cylinder head failure include white smoke from the exhaust (indicating coolant burning), coolant leaks, engine overheating, decreased performance, unusual engine noise, and contaminated oil (milky appearance). You might also notice bubbling in the radiator or overflow tank, sweet-smelling exhaust, or poor fuel economy. If you experience multiple symptoms, have your vehicle inspected immediately to prevent catastrophic engine damage.
What causes cylinder head damage?
The most common causes include engine overheating due to cooling system failures, physical damage from foreign objects, pre-ignition or detonation (engine knock), manufacturing defects, improper maintenance, freeze damage from inadequate antifreeze protection, and age-related fatigue. Overheating is particularly damaging as it can cause warping or cracking. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to warning signs can help prevent most cylinder head problems.
How expensive is it to replace a cylinder head?
Cylinder head replacement costs typically range from $500 to $1,000 for parts alone, depending on vehicle make and model. Labor adds another $500 to $1,500, as the job requires significant disassembly. Total costs can reach $2,000-$3,000 for passenger vehicles and much more for luxury or performance engines. Some situations might require replacing the entire engine if damage is extensive.
How can I maintain my engine’s cylinder head?
Maintain your cylinder head by following regular service intervals for coolant changes to prevent overheating, changing oil on schedule to ensure proper lubrication, avoiding engine overheating by monitoring temperature gauges, addressing small problems before they become serious, using quality fuel to prevent detonation, and warming up your engine properly in cold weather. Have valve adjustments performed as recommended in your vehicle’s service manual.
Can a cracked cylinder head be repaired?
Yes, cracked cylinder heads can sometimes be repaired through welding, metal stitching, or other specialized repair techniques performed by professional machine shops. The success of repairs depends on the crack’s location, size, and severity. Minor cracks in non-critical areas have higher repair success rates. However, extensive cracks or those in high-stress areas often necessitate replacement rather than repair. Always consult with a professional to evaluate repair viability.
How does the cylinder head affect fuel efficiency?
The cylinder head significantly impacts fuel efficiency through its combustion chamber design, which influences how completely fuel burns. Port designs affect airflow efficiency, while valve timing and lift control the precise amount of air-fuel mixture entering the chamber. The compression ratio, partially determined by the cylinder head, directly affects fuel consumption. Modern heads with features like variable valve timing can optimize efficiency across different engine speeds and loads.











