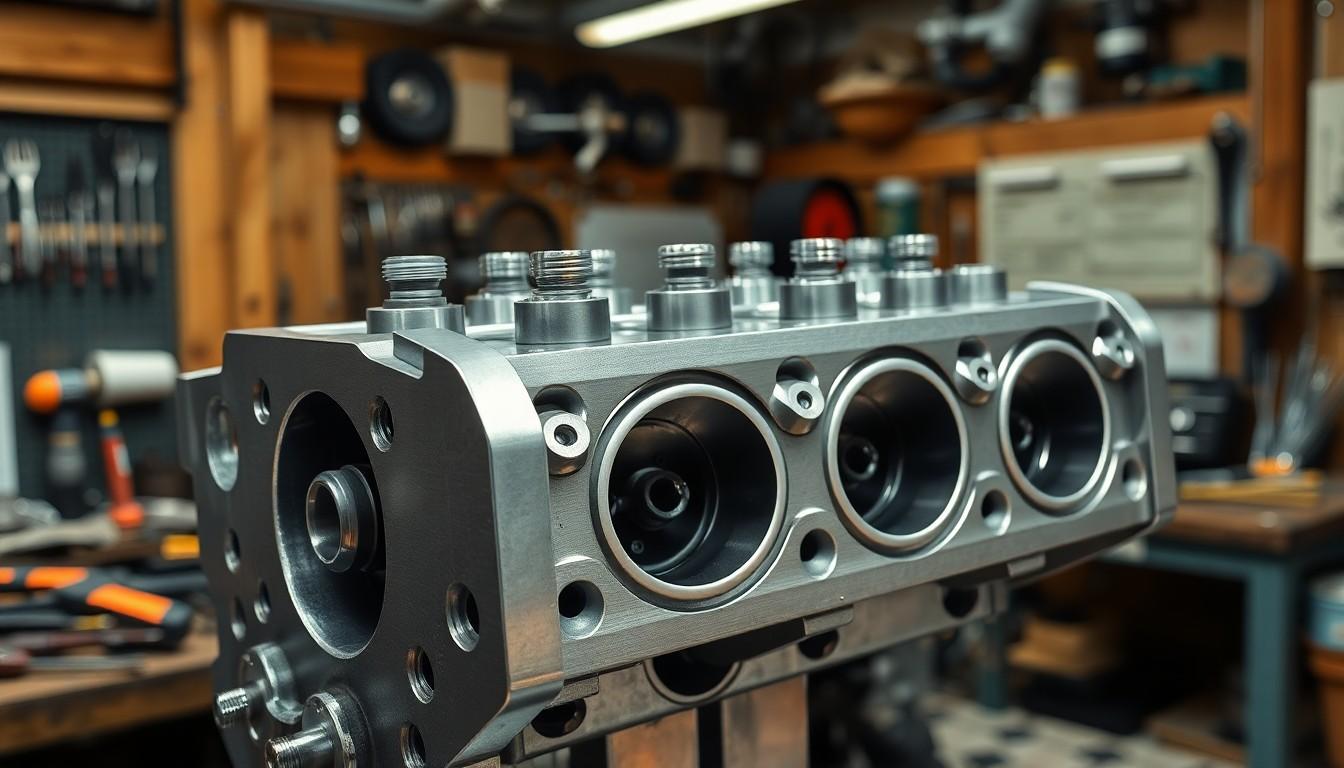
The cylinder head might seem like just another component under your car’s hood, but it’s actually one of the most critical parts of your engine. This complex piece of engineering sits atop the engine block, creating a sealed combustion chamber where the magic of internal combustion happens. Without a properly functioning cylinder head, your vehicle simply wouldn’t run.
We’ve seen countless drivers overlook the importance of this essential component until serious problems arise. That’s why we’ve created this comprehensive guide to explain what the cylinder head does, how it works, and why maintaining it properly can save you thousands in repair costs. Understanding this vital engine part can help you spot potential issues before they leave you stranded on the side of the road.
Understanding the Cylinder Head: A Critical Engine Component
The cylinder head forms the upper section of an engine’s combustion chamber, sealing the top of the cylinders where the combustion process takes place. Located atop the engine block, this precisely engineered component houses several essential elements including intake and exhaust valves, valve springs, camshafts, and spark plugs in gasoline engines or fuel injectors in diesel engines.
Cylinder heads are typically manufactured from aluminum alloy or cast iron, with aluminum being favored in modern vehicles for its lightweight properties and superior heat dissipation capabilities. Cast iron heads, though heavier, offer exceptional durability and heat retention characteristics that benefit certain engine designs.
Modern cylinder heads incorporate water jackets—internal passages that allow coolant to circulate and regulate operating temperatures. These cooling channels prevent overheating and maintain optimal combustion conditions throughout the engine’s operation. Without proper cooling, excessive heat can cause warping, cracking, or complete failure of the cylinder head.
The design of a cylinder head significantly influences an engine’s performance, efficiency, and emissions output. Overhead valve (OHV) designs place the valves in the cylinder head with the camshaft in the block, while overhead cam (OHC) configurations position both valves and camshafts in the cylinder head for improved efficiency. Many performance engines use dual overhead cam (DOHC) setups to maximize airflow and enhance power output across a broader RPM range.
The Primary Functions of a Cylinder Head
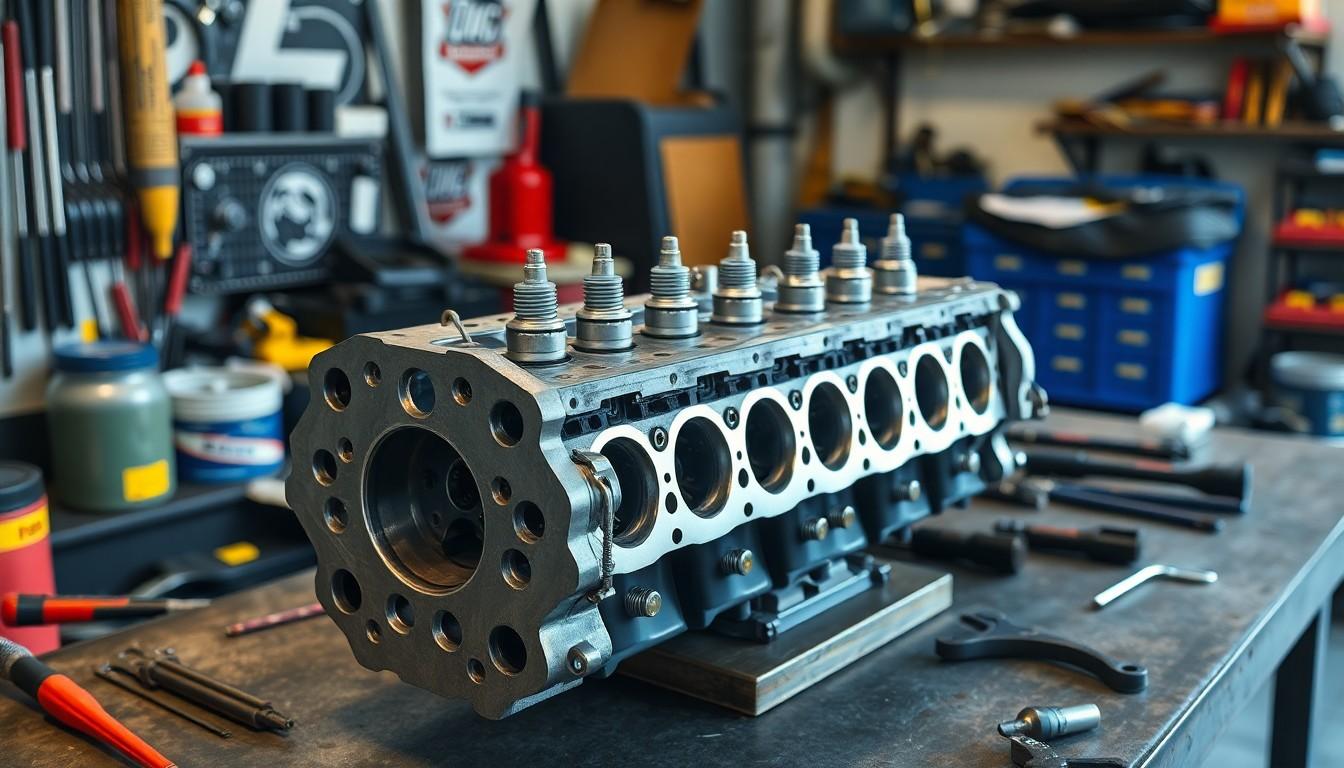
The cylinder head performs several critical functions that directly impact engine performance and efficiency. Let’s examine the three main roles this component plays in your vehicle’s engine system.
Sealing the Combustion Chamber
Cylinder heads create an airtight seal at the top of the combustion chamber, ensuring optimal engine power output. They sit directly on the engine block with a head gasket between them to prevent any leakage during the combustion process. This perfect seal maintains proper compression ratios and allows the engine to generate maximum power from each combustion cycle. The integrity of this seal is essential as any failure here can lead to compression loss, power reduction, and potentially serious engine damage.
Managing Airflow and Exhaust
Cylinder heads control the precise timing and flow of air-fuel mixtures into the cylinders and exhaust gases out of the engine. Their design incorporates specialized pathways called ports that optimize the movement of these gases. The shape, size, and position of these intake and exhaust ports significantly affect an engine’s breathing capability. Better airflow management translates to improved fuel efficiency and enhanced power delivery across different RPM ranges. Performance-oriented cylinder heads often feature ports that have been carefully engineered to maximize flow characteristics.
Housing Valves and Valve Train Components
Cylinder heads contain many vital engine components that work together to regulate engine operation. These components include intake and exhaust valves that control gas flow, spark plugs that ignite the air-fuel mixture, and often the camshafts that orchestrate valve timing. The cylinder head also houses valve springs, valve guides, and retainers that ensure smooth and precise valve movement. The arrangement of these components varies based on engine design, with configurations like overhead valve (OHV) and overhead cam (OHC) determining how the valvetrain operates and eventually affecting engine responsiveness and efficiency.
How Cylinder Heads Affect Engine Performance
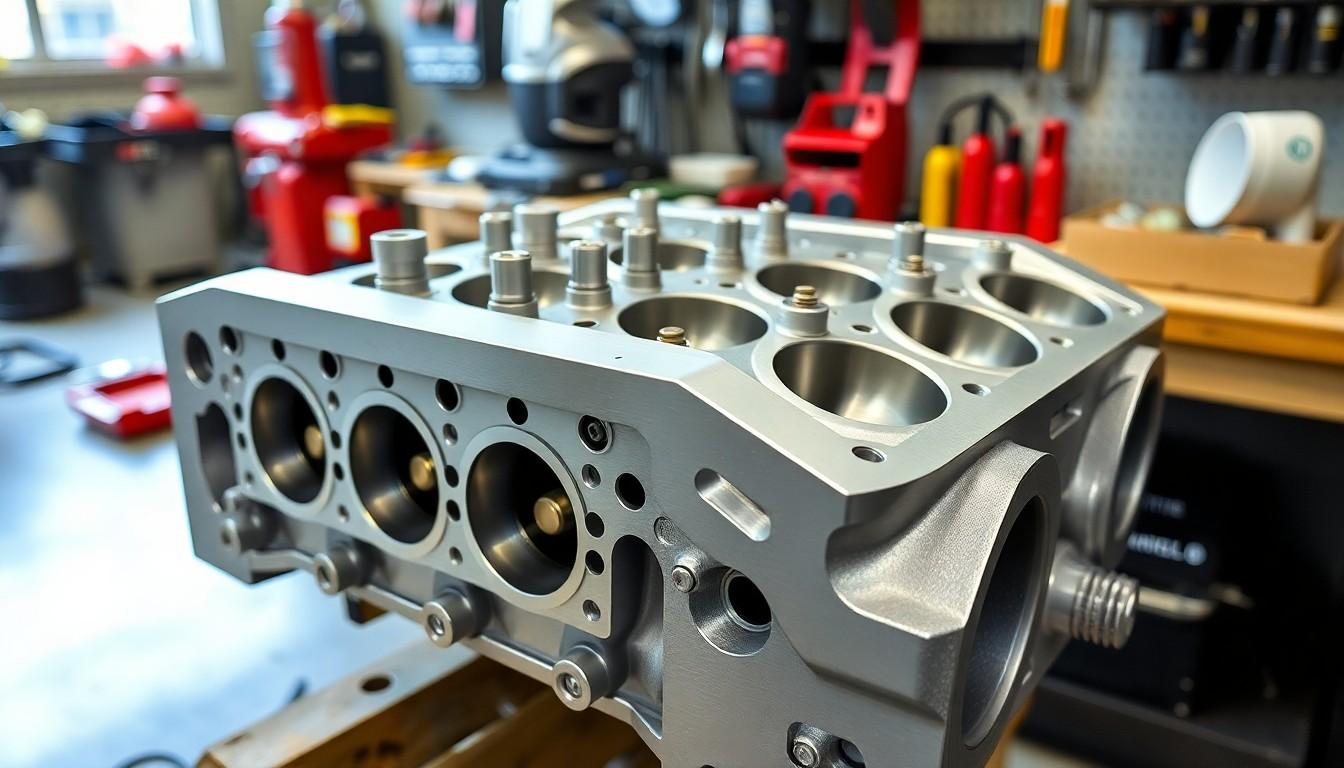

Cylinder heads dramatically influence your vehicle’s overall performance, efficiency, and reliability. Their design and functionality directly impact several critical aspects of engine operation that determine how well your car performs on the road.
Combustion Efficiency and Power Output
Cylinder heads significantly impact combustion efficiency through their chamber design and valve configuration. The shape of the combustion chamber affects how thoroughly fuel and air mix, with more efficient mixing resulting in better power generation and fuel economy. Modern cylinder heads feature precisely engineered chambers that optimize the air-fuel mixture’s burn rate, creating more efficient combustion cycles and increased power output. The positioning of valves within the head determines how effectively air enters and exhaust gases exit the combustion chamber – a critical factor in engine breathing capabilities. Performance cylinder heads often incorporate larger valves, polished ports, and optimized flow paths to enhance airflow by 15-20% compared to stock configurations.
Heat Dissipation Capabilities
Cylinder heads play a crucial role in managing engine temperatures through their integrated cooling systems. These components contain many cooling passages and water jackets that circulate coolant throughout the engine block, preventing overheating issues that can lead to warped heads or blown gaskets. Aluminum cylinder heads, found in 85% of modern vehicles, provide superior heat dissipation compared to cast iron alternatives, dissipating heat up to 3 times faster while reducing overall engine weight. The efficiency of a cylinder head’s cooling design directly correlates with engine longevity and consistent performance, as proper temperature management prevents premature component failure and maintains optimal combustion conditions. Advanced cylinder head designs incorporate targeted cooling around exhaust valve seats and other heat-critical areas, ensuring even temperature distribution throughout the engine.
Cylinder Head Design Variations
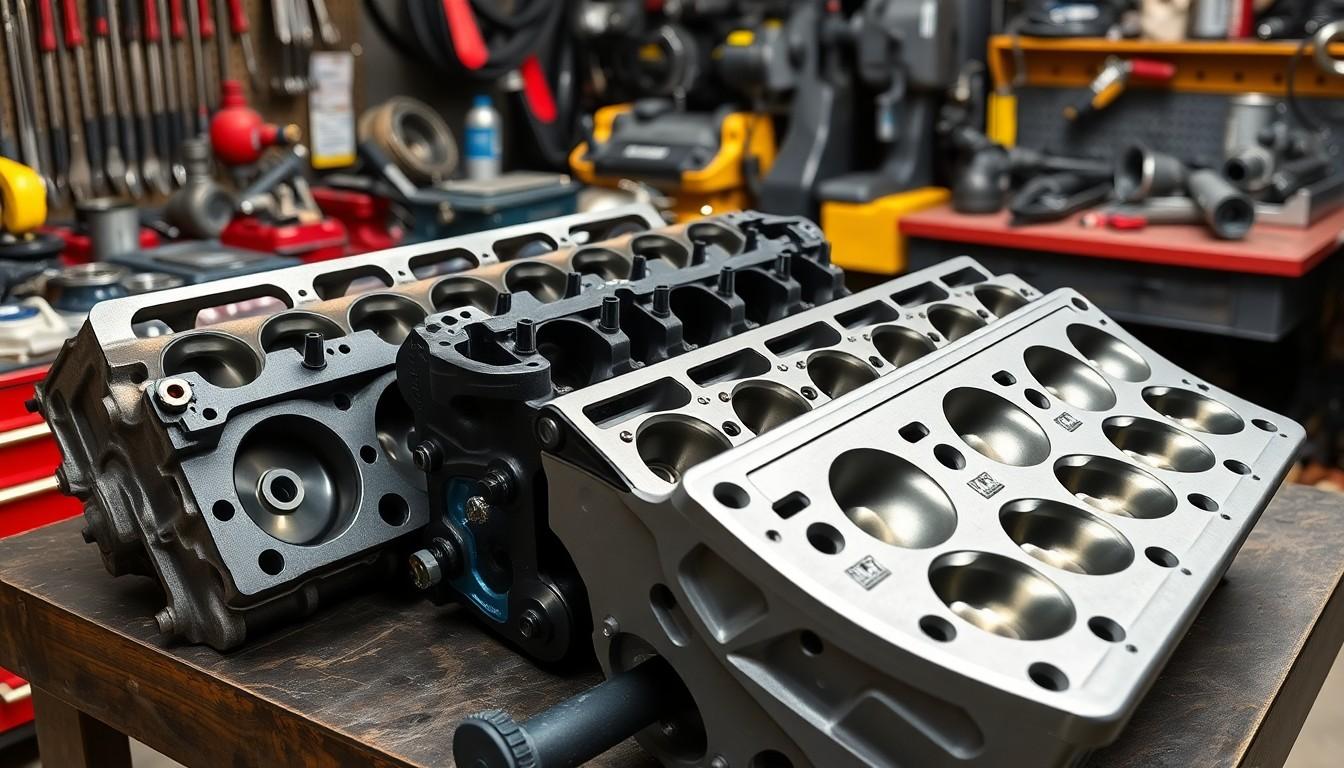

Cylinder head designs vary significantly across different engine types, directly impacting performance, efficiency, and durability. These variations primarily focus on valve arrangement and material composition, which determine how an engine breathes and handles thermal stress.
Overhead Valve (OHV) vs. Overhead Cam (OHC) Designs
OHV engines feature a camshaft located in the engine block that operates valves through a system of lifters, pushrods, and rocker arms. This traditional design offers simplicity and cost-effectiveness for manufacturers but becomes less efficient at higher RPMs due to its complex mechanical linkages. Many classic American V8 engines use this design for its reliability and ease of maintenance.
OHC designs, by contrast, position the camshaft directly above the valves within the cylinder head itself. This configuration eliminates pushrods and reduces moving parts, allowing for quicker valve operation and better performance at higher engine speeds. Modern performance engines often employ OHC designs because they reduce mechanical friction and provide more precise valve timing. Some high-performance variants use dual overhead cams (DOHC), with separate camshafts for intake and exhaust valves, maximizing airflow potential and power output.
Material Differences: Cast Iron vs. Aluminum
Cast iron cylinder heads deliver exceptional durability and resistance to thermal distortion under high pressures and temperatures. Their robust nature makes them ideal for heavy-duty applications where longevity trumps weight considerations. Cast iron retains heat effectively, which can improve combustion efficiency in cold conditions, but its lower thermal conductivity may contribute to localized hot spots and less efficient cooling overall.
Aluminum cylinder heads weigh approximately 50% less than their cast iron counterparts, significantly reducing the engine’s overall weight and improving vehicle performance and fuel economy. Their superior thermal conductivity allows heat to dissipate more quickly, improving cooling efficiency and reducing the risk of detonation or pre-ignition. Aluminum heads typically incorporate hardened valve seats and specialized coatings to compensate for the material’s naturally lower wear resistance compared to cast iron. Most modern engines use aluminum cylinder heads with sophisticated cooling passages to optimize performance while maintaining appropriate operating temperatures.
Common Cylinder Head Problems and Symptoms

Cylinder heads can experience several issues that affect engine performance and longevity. Understanding these problems helps vehicle owners identify potential issues before they cause severe engine damage.
Overheating and Warping Issues
Overheating is one of the most common cylinder head problems, often leading to warping of this crucial component. A malfunctioning cooling system, blocked radiator, or faulty thermostat typically causes excessive heat buildup in the engine. Improper head gasket installation or misalignment between the engine block and head can also contribute to warping problems. Engine temperature rising substantially above normal operating levels serves as the first warning sign of overheating. Coolant leaks may become visible around the cylinder head area, indicating potential warping. Severe cases result in engine stalling or failure to start altogether, requiring immediate attention to prevent permanent damage.
Cracked Cylinder Head Warning Signs
Cracks in cylinder heads develop from multiple factors including prolonged overheating, misalignment issues, or manufacturing defects. Coolant leaking into the oil system or combustion chamber represents a clear indicator of cylinder head cracks. Oil contamination in the cooling system often appears as a milky substance in the radiator or overflow tank. White smoke emanating from the exhaust pipe signals coolant burning in the combustion chamber due to cracks. Engine performance noticeably decreases with power loss and rough idling as common symptoms. Persistent overheating even though a functioning cooling system strongly suggests cylinder head problems. Vehicles experiencing these symptoms may eventually stall or fail to start, signaling critical damage requiring professional diagnosis and repair.
Cylinder Head Maintenance and Replacement

Proper cylinder head maintenance prevents costly engine problems and extends vehicle lifespan. Regular care and timely intervention can save thousands in repair costs while maintaining optimal engine performance.
Cylinder Head Maintenance
Regular maintenance of cylinder heads is essential for preventing serious engine issues. Checking for oil leaks around the cylinder head gasket helps identify potential seal failures before they cause major damage. Monitoring engine temperature during operation allows early detection of cooling system problems that might affect the cylinder head. Inspecting the cylinder head for visible cracks or damage during routine service intervals can catch developing issues. Professional mechanics recommend cleaning carbon deposits from valve seats and ports every 30,000 miles to maintain proper airflow and combustion efficiency.
Proper coolant maintenance directly impacts cylinder head longevity by preventing overheating and corrosion. Using manufacturer-recommended coolant types and maintaining proper levels protects the internal cooling passages from scale buildup and deterioration. Addressing unusual engine noises promptly can prevent minor valve train issues from escalating into major cylinder head damage. Timing belt or chain maintenance also prevents catastrophic cylinder head damage that occurs when these components fail during operation.
When to Consider Rebuilding vs. Replacing
Rebuilding cylinder heads offers important cost advantages in many situations. Professional rebuilding typically costs 40-60% less than complete replacement while restoring original specifications and performance. Minor issues like worn valve guides, damaged valve seats, or surface warping under 0.004 inches make excellent candidates for rebuilding rather than replacement. Original factory cylinder heads often feature superior casting quality compared to aftermarket replacements, making them worth salvaging through proper rebuilding techniques.
Replacing cylinder heads becomes necessary under exact circumstances even though higher costs. Severe cracks that penetrate water jackets or combustion chambers render rebuilding impossible due to structural integrity concerns. Extensive erosion damage from prolonged overheating or combustion issues can thin cylinder head walls beyond safe limits. Performance upgrades sometimes justify complete replacement with heads designed for improved flow characteristics, higher compression ratios, or different valve arrangements. Newer vehicle models with integrated components like camshafts or variable valve timing systems often require complete assembly replacement rather than rebuilding individual components.
Conclusion
The cylinder head stands as one of the most critical components in your vehicle’s engine system. Without proper function your engine simply can’t deliver the performance efficiency and reliability you expect. By understanding its role in sealing the combustion chamber managing airflow and housing essential components you’re better equipped to recognize potential issues before they become expensive problems.
Regular maintenance checks and prompt attention to warning signs like overheating or unusual smoke can save thousands in repair costs. Whether you’re dealing with an OHV or OHC design aluminum or cast iron construction the principles remain the same – your cylinder head deserves attention and care.
Remember that proper cylinder head maintenance isn’t just about avoiding repairs it’s about maximizing your engine’s performance and extending your vehicle’s lifespan.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a cylinder head and why is it important?
A cylinder head is a critical engine component that forms the upper section of the combustion chamber. It houses vital elements like valves, camshafts, and spark plugs while creating a sealed environment for combustion. Its importance lies in its role in managing airflow, exhaust, and temperature regulation, directly impacting engine performance, efficiency, and reliability. Without a properly functioning cylinder head, an engine cannot maintain compression or operate effectively.
What materials are used to make cylinder heads?
Modern cylinder heads are primarily made from aluminum or cast iron. Aluminum heads are lightweight with excellent heat dissipation properties, improving fuel efficiency and performance. Cast iron heads offer superior durability and heat retention but add weight to the engine. Each material has specific advantages depending on the vehicle’s intended use, with aluminum being the preferred choice in most contemporary engines due to its thermal conductivity.
How does cylinder head design affect engine performance?
Cylinder head design significantly impacts engine performance through valve arrangement, port shape, and combustion chamber design. Overhead valve (OHV) designs are simpler but less efficient at high RPMs than overhead cam (OHC) designs, which allow quicker valve operation. Dual overhead cam (DOHC) setups maximize airflow and power. The design influences combustion efficiency, power output, and the engine’s breathing capability, directly affecting overall vehicle performance.
What are the most common cylinder head problems?
The most common cylinder head problems include overheating and warping (often from cooling system failures), cracking (from prolonged overheating or misalignment), valve and seat wear, and gasket failure. These issues typically manifest through symptoms like rising engine temperatures, coolant leaks, white exhaust smoke, oil contamination, and decreased engine performance. Early detection of these problems is crucial to prevent catastrophic engine damage.
What are the signs of a failing cylinder head?
Signs of a failing cylinder head include engine overheating, white smoke from the exhaust (indicating burning coolant), coolant mixing with oil (milky appearance), decreased engine performance, and visible coolant leaks. You might also notice poor fuel economy, rough idling, or engine misfires. If you experience any of these symptoms, immediate professional diagnosis is recommended to prevent more severe engine damage.
How can I maintain my engine’s cylinder head?
Maintain your cylinder head by regularly checking for oil leaks, monitoring engine temperature, and ensuring proper coolant levels with the correct antifreeze mixture. Avoid overheating by addressing cooling system issues promptly. Follow your vehicle’s recommended maintenance schedule for coolant flushes. Clean carbon deposits from valve seats periodically and have comprehensive inspections during major service intervals. Proper maintenance significantly extends the lifespan of your cylinder head.
When should I rebuild vs. replace a cylinder head?
Rebuild your cylinder head when it has minor issues like small cracks, worn valve seats, or warping within repairable limits. This option is typically more cost-effective. Consider replacement when the head has severe cracking, extensive warping beyond machining tolerance, or structural damage. The decision should balance repair costs against the cylinder head’s value and availability. Original factory heads often have superior quality worth salvaging through rebuilding.
How does a cylinder head regulate engine temperature?
A cylinder head regulates engine temperature through integrated water jackets—passages that allow coolant to circulate around the combustion chambers. These channels absorb and dissipate heat generated during combustion, preventing overheating. Aluminum cylinder heads provide better heat dissipation than cast iron due to superior thermal conductivity. This cooling system is crucial for maintaining optimal operating temperatures, preventing warping, and ensuring consistent engine performance and longevity.