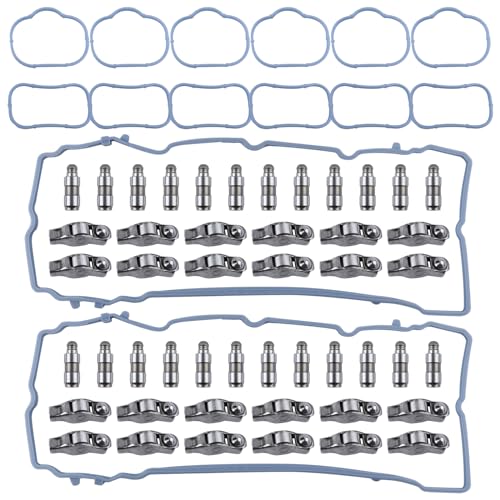
Ever wondered what makes your engine run so smoothly? The car rocker arm might be small, but it’s one of the unsung heroes under your hood. We’ve seen countless drivers overlook this critical component until performance issues arise.
These pivotal mechanical parts transfer motion from the camshaft to the valves, controlling the precise timing of your engine’s breathing. Without properly functioning rocker arms, your vehicle wouldn’t deliver the reliable performance you’ve come to expect. They’re essentially the middlemen in your engine’s complex valve train system, translating rotational movement into the linear action that powers your car forward.
What Is a Car Rocker Arm: Function and Purpose
A car rocker arm operates as a pivoting lever that transfers motion from the camshaft to the engine’s valves. This small component plays a critical role in the valve train system by converting the rotational movement of the camshaft into the linear motion needed to open and close intake and exhaust valves. Rocker arms ensure precise valve timing, which directly impacts engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
The primary function of rocker arms involves creating mechanical advantage through leverage, multiplying the force from the camshaft to effectively open valves against strong valve spring pressure. These components work in a continuous cycle—as the camshaft lobe rotates, it pushes up on one end of the rocker arm, causing the opposite end to press down on the valve stem, which opens the valve to allow air/fuel mixture in or exhaust gases out.
Modern engines use various rocker arm configurations, including:
- Shaft-mounted rockers: Attached to a common shaft for stability and consistent operation
- Pedestal-mounted rockers: Individually mounted on pedestals bolted to the cylinder head
- Roller rockers: Feature roller bearings that reduce friction and improve efficiency
- Stamped steel rockers: Lightweight, cost-effective options common in many production vehicles
Rocker arms maintain the delicate balance between durability and performance by being constructed from materials strong enough to withstand tremendous forces yet light enough to minimize reciprocating mass. Their design incorporates precise geometry to establish the correct valve lift and timing relationship necessary for optimal engine operation.
Anatomy of a Rocker Arm System
The rocker arm system forms a critical linkage in the engine’s valvetrain, translating rotational motion into linear valve action. This mechanical symphony involves multiple components working in perfect coordination to manage airflow into and out of the combustion chamber.
Types of Rocker Arms
Standard rocker arms operate as simple pivoting levers in overhead valve (OHV) engines, transferring motion from pushrods to valve stems. Roller rockers incorporate precision bearings at contact points between the rocker and valve stem or cam lobe, reducing friction by up to 50% compared to standard designs. Finger followers serve as specialized short rocker arms commonly found in overhead cam (OHC) engines, pivoting on roller bearings while the cam lobe pushes downward on their back surface. Shaft-mounted rocker arms provide enhanced stability at higher RPMs by mounting multiple rockers on a common shaft rather than individual pedestals. Each design offers different performance characteristics, with roller rockers particularly favored in high-performance and racing applications due to their reduced friction and ability to handle increased engine speeds.
Materials Used in Modern Rocker Arms
Stamped steel dominates standard rocker arm construction in production vehicles, offering an optimal balance of durability and cost-effectiveness. Aluminum alloy rockers weigh approximately 30% less than their steel counterparts, making them ideal for high-revving applications where reduced reciprocating mass improves engine response. High-quality chromoly and alloy steels provide exceptional strength in performance applications, withstanding extreme valve spring pressures and elevated temperatures. Cast iron rockers, though heavier, still appear in some heavy-duty applications where durability trumps weight concerns. Composite materials have emerged in cutting-edge designs, combining lightweight properties with excellent heat resistance. Material selection significantly impacts not only the rocker arm’s longevity but also affects overall engine efficiency, with lightweight options enabling quicker valve actuation and potentially improving fuel economy in properly designed systems.
How Rocker Arms Work in the Valve Train
Rocker arms play a vital role in transferring motion within an engine’s valve train system. They act as mechanical bridges, ensuring precise timing and operation of the valves during the combustion process.
Mechanism
In overhead valve (OHV) engines, the mechanism follows a sequential process. The camshaft rotates and pushes the pushrod upwards with each cam lobe movement. This upward motion of the pushrod then pushes one side of the rocker arm. As the rocker arm pivots around its fulcrum point, the opposite end presses down on the valve stem, opening the valve against spring tension.
Overhead cam (OHC) engines operate slightly differently. Short rocker arms or finger followers are utilized when the cam lobe pushes directly downward on the back of the rocker arm. These followers pivot on roller bearings and press against the top of the valve stem, compressing it with the force transmitted from the cam lobe.
The synchronized movement between these components creates a reliable valve actuation system. Every millisecond of this operation is precisely calculated to optimize air intake and exhaust flow during each engine cycle.
The Mechanical Advantage of Rocker Arms
Rocker arms provide several critical mechanical advantages in modern engines. They efficiently transfer rotational motion from the camshaft into the linear motion needed for valve operation, acting as a motion conversion device.
Friction reduction represents another important benefit, particularly in roller rocker designs. These specialized rockers incorporate bearings at contact points, minimizing wear on valve components and allowing engines to operate at higher RPMs without sacrificing reliability.
The geometry of rocker arms can be engineered to create different leverage ratios, affecting valve lift and timing characteristics. This adjustability gives engine designers greater control over performance parameters and combustion efficiency.
Modern rocker arms, constructed from high-quality alloy steels or aluminum, ensure strength and durability under extreme operating conditions. Their robust construction maintains engine integrity through millions of operating cycles, contributing significantly to overall powertrain longevity and performance.
Common Rocker Arm Problems and Symptoms
Rocker arm issues can significantly impact engine performance and longevity. These pivotal components face constant stress during engine operation, making them susceptible to various problems over time.
Worn Rocker Arms
Worn rocker arms manifest through several telltale symptoms that indicate valvetrain deterioration. Increased engine noise, particularly a distinctive tapping or clattering sound, often serves as the first warning sign of rocker arm wear. Engine performance noticeably declines as worn components fail to help proper valve timing, resulting in decreased power and reduced fuel efficiency during operation.
Oil consumption typically increases when worn rocker arms allow lubricant to seep into the combustion chamber, compromising the engine’s ability to maintain proper oil levels. Engines with worn rocker arms frequently experience overheating issues because improperly opening and closing valves directly affect the cooling system’s efficiency.
Several factors contribute to rocker arm wear, including accumulated high mileage and natural degradation over time. Inadequate maintenance practices, especially infrequent oil changes, accelerate the deterioration process by allowing contaminants to damage the metal surfaces. Using incorrect or low-quality lubricants creates insufficient protection for these critical components under high-stress conditions. Performance driving and racing applications place extreme demands on rocker arms, dramatically shortening their effective lifespan compared to normal driving conditions.
Broken or Bent Rocker Arms
Broken or bent rocker arms create more severe symptoms than merely worn components. Severe engine noise, characterized by loud clattering or banging sounds, indicates catastrophic rocker arm failure requiring immediate attention. Engine misfires become common as the damaged rocker arm prevents proper valve operation, sometimes rendering the vehicle completely inoperable.
Visual inspection often reveals obvious signs of damage including oil leaks around the valve cover and physical deformation of the affected rocker arms. Continued operation with broken rocker arms risks cascading damage to other engine components, potentially leading to complete engine failure if left unaddressed.
Physical impacts and collisions rank among the primary causes of bent or broken rocker arms, particularly in off-road applications. Exceeding the engine’s RPM limits puts tremendous stress on the valvetrain, potentially causing rocker arm failure under extreme conditions. Improper installation or incorrect adjustment during maintenance can create misalignment issues that eventually lead to component failure. Failures in related components such as lifters or pushrods transfer excessive force to the rocker arms, often resulting in breakage even when the rocker arms themselves were initially in good condition.
Maintenance and Replacement of Rocker Arms
Rocker arms require periodic maintenance and eventual replacement to ensure optimal engine performance. These critical valvetrain components experience considerable stress and wear during normal engine operation, making their upkeep essential for long-term engine health.
Signs for Replacement
Engine noise often serves as the first indicator of rocker arm issues, particularly ticking or clicking sounds that become more pronounced during acceleration. Performance problems such as reduced power, rough idling, or decreased fuel efficiency frequently point to worn or damaged rocker arms affecting proper valve operation. Oil leaks around the valve cover area suggest deteriorating rocker arm seals or components. Visual inspection may reveal pitting, scoring, or excessive wear on rocker arm surfaces, especially at contact points with pushrods and valve stems. Misfiring cylinders sometimes indicate a rocker arm that’s no longer providing adequate valve actuation, disrupting the combustion process.
When to Replace Your Rocker Arms
High mileage vehicles typically need rocker arm replacement between 50,000 and 100,000 miles, depending on driving conditions and maintenance history. Engine overhauls present the perfect opportunity to install new rocker arms, ensuring all valvetrain components work harmoniously. Performance upgrades often necessitate rocker arm replacement, with roller rockers offering reduced friction and improved efficiency compared to standard components. Unusual engine noises demand immediate inspection of the rocker arms, as continued operation with damaged components can lead to more extensive engine damage. Regular oil changes with quality lubricants can extend rocker arm life substantially, though even well-maintained components eventually require replacement due to normal wear.
Replacement Process
Accessing rocker arms begins with removing the valve cover, which typically involves loosening several bolts and breaking the gasket seal carefully. Pushrods must be removed and organized in their exact original positions to maintain proper engine timing during reassembly. Loosening and removing the rocker arm nuts or bolts requires proper torque specifications and sequence to prevent warping components. Installing new rocker arms demands careful alignment with pushrods and valve stems, plus precise torque application according to manufacturer specifications. Reassembly follows the reverse order of disassembly, with special attention to proper gasket seating and torque specifications on all fasteners. Professional replacement ensures proper valve adjustment and prevents potential timing issues that could damage the engine.
Performance Upgrades and Modifications
Upgrading your car’s rocker arms can significantly enhance engine performance and durability. These modifications allow engines to operate at higher RPMs while reducing friction and wear on critical components.
Roller Rockers
Roller rockers represent one of the most popular performance upgrades for vehicle valve trains. These specialized components incorporate needle bearings or a single bearing ball at the valve contact point, drastically reducing friction compared to standard rocker arms. Originally developed for racing applications, roller rockers have become more accessible to everyday performance enthusiasts. The reduced friction allows engines to reach higher RPMs more efficiently, creating noticeable power gains especially in high-revving scenarios. Many performance shops report that replacing standard rockers with roller variants can free up 5-15 horsepower in properly tuned engines.
Materials
Material selection plays a crucial role in rocker arm performance and longevity. High-performance rocker arms use premium alloy steels that offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios. Aluminum rocker arms have gained popularity in performance applications due to their lightweight properties and heat dissipation capabilities. These aluminum variants typically reduce valvetrain weight by 40-60% compared to standard steel rockers, allowing for quicker valve operation and reduced stress on valve springs. Racing-grade rockers often incorporate specialized heat treatments and coatings to withstand extreme conditions, ensuring consistent performance even under high-stress situations.
Design Variations
Modern engines feature many rocker arm design variations optimized for exact performance goals. OHC engines frequently employ short rocker arms or finger followers where the cam lobe applies downward pressure directly on the rocker back. This design reduces reciprocating mass and allows for more precise valve control at high engine speeds. Performance-oriented designs also feature optimized geometry with carefully calculated ratios between the pushrod side and valve side. Some advanced designs include adjustable rocker ratios, allowing fine-tuning of valve lift without changing camshafts. These adjustable systems provide tuners with additional flexibility when maximizing engine performance for exact applications like drag racing, circuit racing, or street performance.
Conclusion
Rocker arms may be small but they’re mighty contributors to your engine’s performance. They serve as critical mechanical bridges ensuring valves open and close with precision timing. Without them your engine simply couldn’t function properly.
We’ve seen how different materials and designs offer various benefits from basic functionality to high-performance applications. Understanding these components helps diagnose potential issues before they become major problems.
Whether you’re maintaining your daily driver or upgrading a performance vehicle proper attention to your rocker arms pays dividends in engine longevity and efficiency. As automotive technology continues to advance these humble components remain essential to the heartbeat of your vehicle’s powertrain.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a car rocker arm and what does it do?
A car rocker arm is a pivoting lever in the engine’s valve train that converts the camshaft’s rotational movement into linear motion. It transfers this motion to open and close the intake and exhaust valves with precise timing. This small but crucial component ensures proper engine combustion, directly affecting performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
How do I know if my rocker arms are failing?
Signs of failing rocker arms include unusual engine noise (particularly ticking or clicking sounds), decreased engine power, reduced fuel efficiency, and engine misfires. You might also notice engine overheating issues or oil leaks around the valve cover. Any of these symptoms warrant immediate inspection by a qualified mechanic.
How often should rocker arms be replaced?
Rocker arms typically need replacement between 50,000 and 100,000 miles, depending on driving conditions and maintenance history. They should be inspected during routine valve adjustments and replaced if showing signs of wear, such as pitting, scoring, or excessive movement. Engine overhauls or performance upgrades are ideal times for preventive replacement.
What are roller rocker arms and are they worth upgrading to?
Roller rocker arms feature roller tips that reduce friction against the valve stems, allowing for smoother operation and higher RPM capability. This upgrade can increase horsepower, improve throttle response, and reduce valve train wear. For performance enthusiasts, the benefits often justify the cost, but they may not be necessary for standard daily driving.
What materials are used in modern rocker arms?
Modern rocker arms are made from various materials including stamped steel (most common in standard vehicles), aluminum alloys (lighter weight for high-revving engines), and high-quality chromoly steel (for performance applications). Newer composite materials are also emerging in cutting-edge designs. Material choice affects durability, performance, and price.
Can I replace rocker arms myself?
While DIY replacement is possible for experienced home mechanics, professional installation is recommended. The process requires specialized tools, precise torque specifications, and proper valve adjustment skills. Incorrect installation can lead to serious engine damage, timing issues, and costly repairs. Always consult your vehicle’s service manual if attempting this repair.
What is the rocker arm ratio and why does it matter?
The rocker arm ratio is the relationship between the distances from the pivot point to the valve stem and from the pivot to the pushrod or cam lobe. This ratio determines valve lift and affects engine performance characteristics. Higher ratios increase valve lift, potentially improving airflow and power, but may require additional modifications to maintain reliability.
How do rocker arms differ between OHV and OHC engines?
In overhead valve (OHV) engines, rocker arms work with pushrods to transfer motion from the camshaft to the valves. In overhead cam (OHC) engines, shorter rocker arms or finger followers interact directly with the camshaft. OHC designs typically allow for higher RPM operation and more precise valve timing due to fewer moving parts.